Did City Link’s customer reviews predict failure?
Customer experience reviews are a rich source of information for companies wanting to improve. They also contain vital signals for companies needing to survive.
On Christmas Eve, the UK parcel courier City Link delivered itself into administration. A few days later on New Year’s Eve, the absence of anyone wishing to pay the right price to pick up the pieces dealt the final blow. The company collapsed and took with it the jobs of over 2,300 people. Timing – whether delivering parcels or news – would sadly not appear to be one of their strong points.

Being aware of the changing environment is key to survival
Could they have seen it coming? Maybe they did, but it sends a message to other companies that the early warning signs of trouble and what needs to change are not hidden away in an elusive, impenetrable vault. Customers themselves are a reliable barometer of the pressure a business is under. A quick look back at City Link’s customer reviews in the months and weeks leading up to the company’s failure should have set alarm bells ringing far beyond learning about niggles and gripes.
Take what was being said on Trustpilot for example. There, just under 1,300 customers have taken the time and trouble to share their thoughts. 69% of them gave a 1-star rating; 22% gave 5 stars. So while some things were being done right, there was clearly a dangerous groundswell of very unhappy customers.
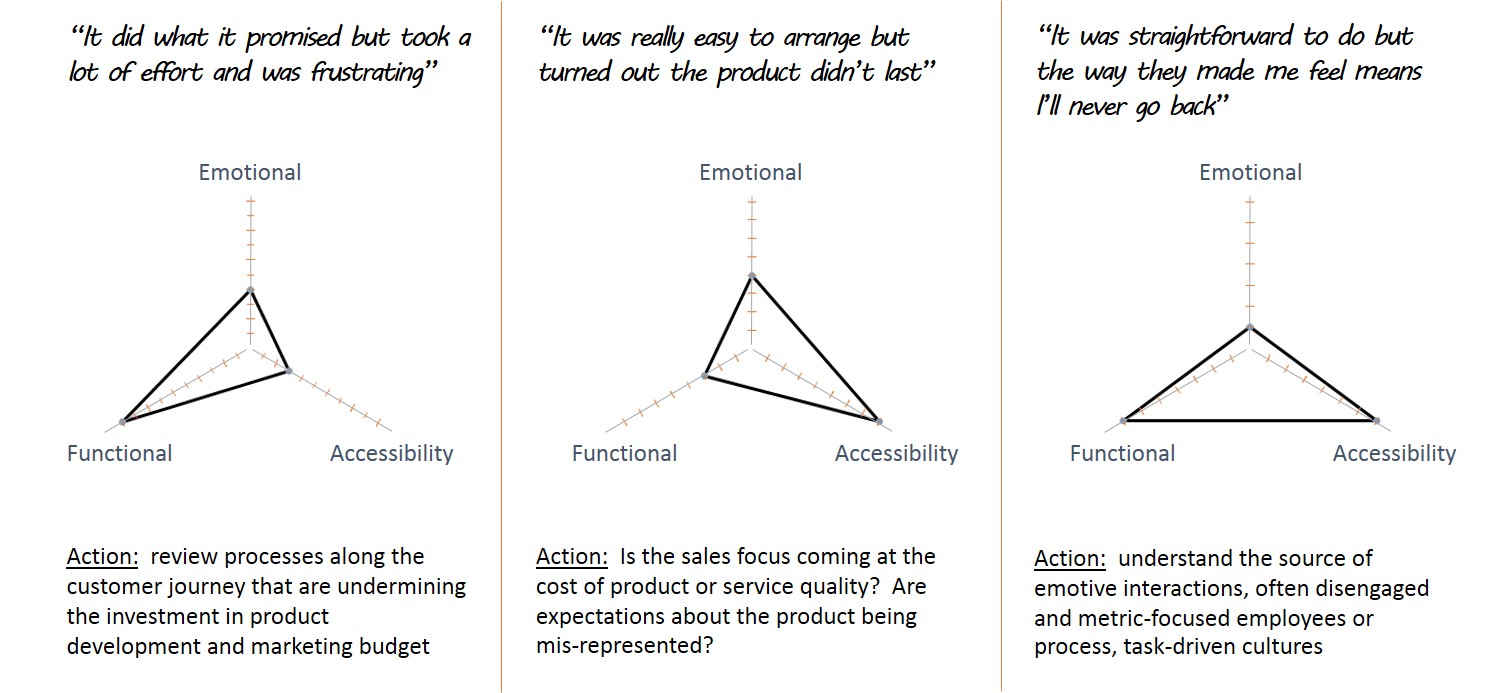
Scores are one thing; more telling is the level of negative emotion that customers talked about. Over two-thirds of their customer reviews were not just people with a complaint; the depth of emotion about their experience was raw and they made sure other customers knew about it. Other review sites are available but if you want to read what customers said on Trustpilot about being on the receiving end of the wrong customer experiences, click here.
In short, the problem was not that customers felt underwhelmed by the lack of any “wow” experiences. Of greater concern was the lack of basic expectations – unmet promises, conflicting information and being treated with contempt by rude staff. Things that are arguably not hugely expensive to put right, but all of which created a lack of trust and customers warning other customers not to use them.
City Link was owned by a private equity firm who will have had a clear idea of what they wanted in return for their investment. It’s not my money that’s at stake so I’m not in a position to pass comment on the business decisions and focus. But, those reporting on the collapse cite operational efficiencies and intense competition as key reasons for the demise. And while neither issue is insignificant it will be rare to find a business that doesn’t share the same challenges. Worse still, customers have been shouting about the solutions from the pages of review sites.
I’m privileged to work with a variety of organisations across a variety of markets and countries. It’s also my job to learn from others who are pushing the bar higher or dragging the bar up to where it needs to be to survive. I see three factors that are common in many cases, and with City Link here too. One: detail. People talk about surprise and delight, exceeding expectations. Nice idea, but “WOW” stands for a complete Waste of Work and cost if the basics are not in place. Two: consistency. Those basics need to work time after time, whoever, wherever and however the experience is being delivered. Three: listen. Customers are saying what can, and needs to, improve.
So as we finish our reflections on last year and head into the new full of ambition, maybe first up on our 2015 to-do list is to make sure we’re listening properly and acting on the right things that will ensure there is a business for customers and employees to come back to.